Mitchell’s EV Collision Insights 2023 Year in Review
Mitchell International, a provider of electric vehicle trends and data for auto insurers and collision repairers, released “Plugged-In: EV Collision Insights 2023 Year in Review,” authored by Ryan Mandell, Mitchell International’s Director, Performance Consulting.
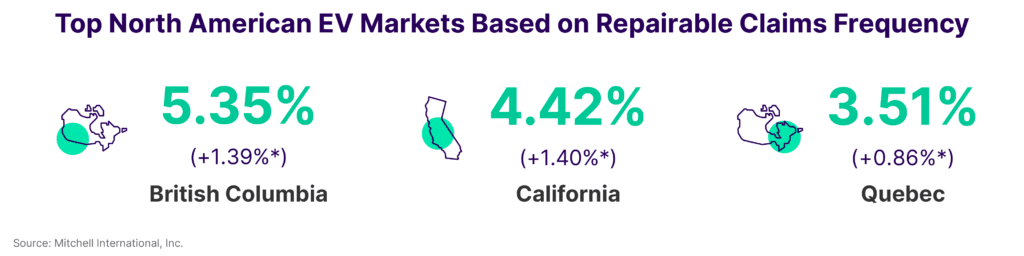
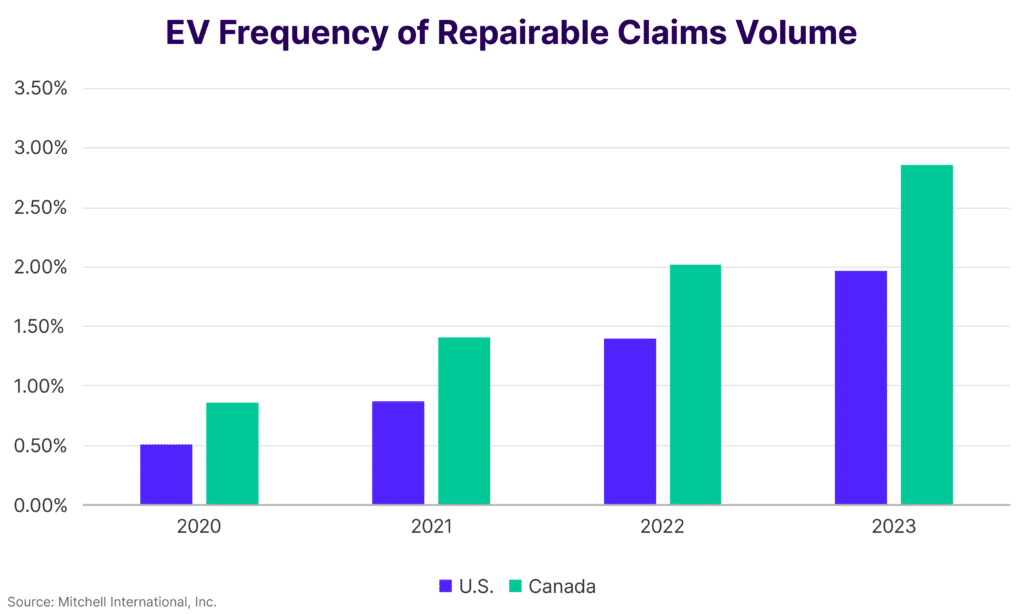
In 2023, the landscape of electric vehicle (EV) repairable claims saw significant shifts in the United States and Canada, marking a pivotal moment in the industry. The frequency of repairable claims for EVs ended the year at 1.97% in the United States and 2.86% in Canada, signaling an increase of over 40% in both regions compared to the previous year. This escalation, stark in its comparison, indicates that the frequency of claims has more than tripled since 2020.
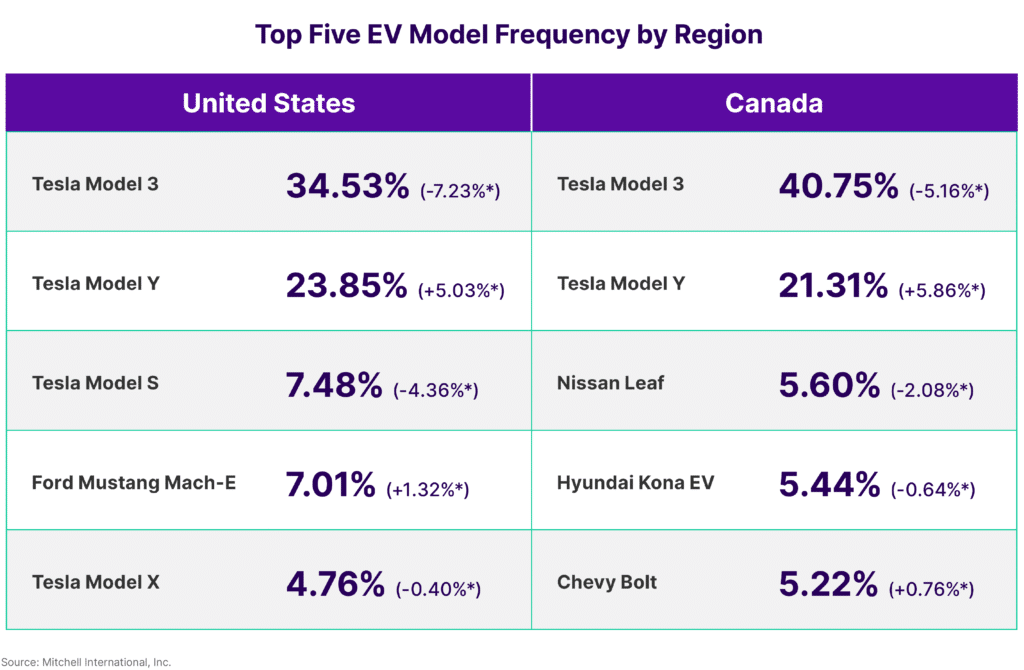
Amidst these changes, Tesla’s presence in the U.S. market reached new heights, with its share of total new vehicle sales climbing to a record 4.2%. Nonetheless, the year also witnessed the emergence of lower priced EV models, such as the Kia EV6, Hyundai Ioniq, and Volkswagen ID.4, which saw astonishing growth rates of 194%, 144%, and 139% respectively. This surge in popularity for alternative EV options, coupled with the introduction of other new models, poses a formidable challenge to Tesla’s previously unchallenged market dominance.
“2023 was a record year for electric vehicles,” said Ryan Mandell, Mitchell’s director of claims performance. “Not only did the frequency of EV collision claims rise to historic levels but the U.S. also surpassed 1.2 million in new EV sales for the first time ever. As long as consumer adoption remains strong, EVs will continue to have a significant impact on the auto insurance industry—creating challenges for everything from underwriting to the delivery of proper and safe repairs.”
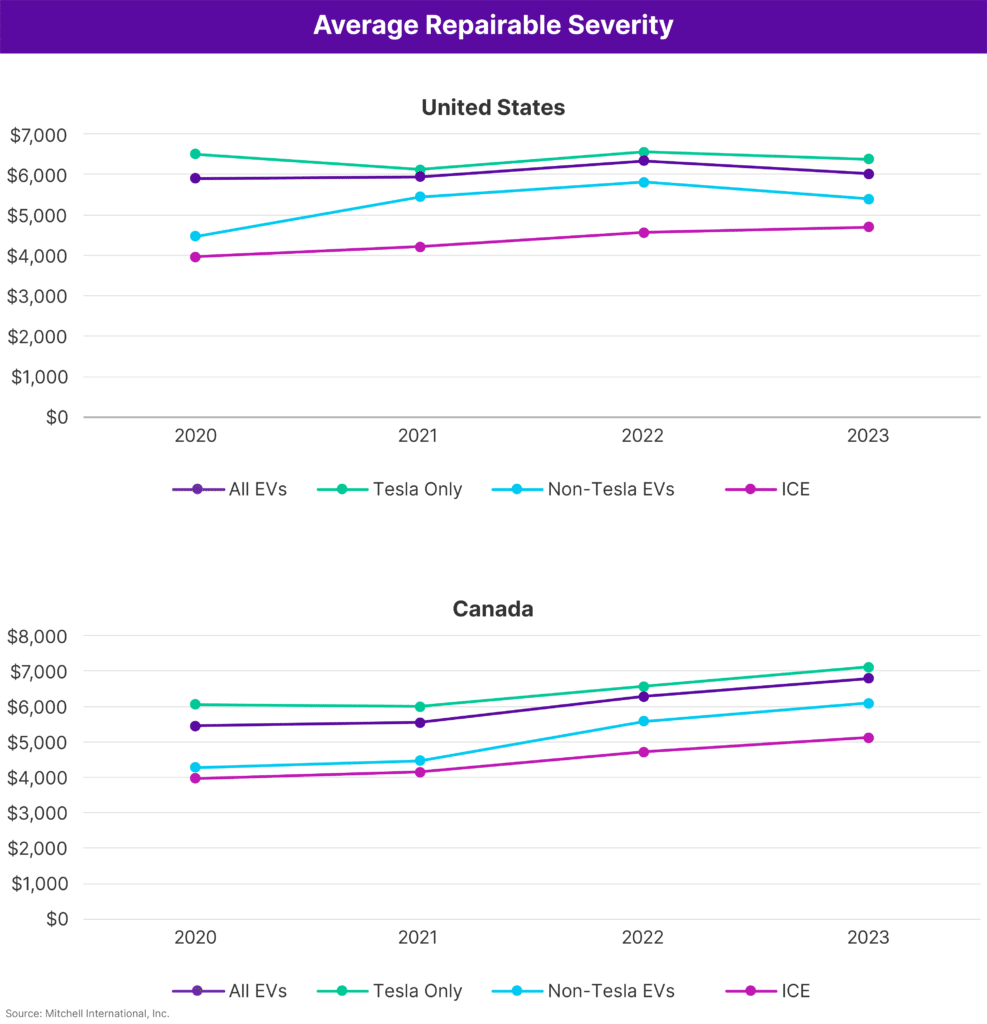
In terms of claims severity, EVs continued to exhibit a higher cost in repairs compared to their ICE counterparts. In the U.S. during the last year, the average cost for EV repairable claims stood prominently at $6,018, markedly exceeding the $4,696 average for ICE vehicles, illustrating a notable difference of $1,322. Despite this disparity, the repair costs for EVs saw a slight decrease, dipping by about 5% from the previous year, while ICE-powered vehicles experienced a 3% climb in repair severity. This trend mirrored in Canada, with average EV repair costs reaching $6,795 (CAD), and ICE vehicles at $5,122 (CAD). However, contrasting with the American scenario, Canadian figures witnessed an approximate 8% surge across both categories, from 2022 to 2023, highlighting a consistent rise in repair costs irrespective of the power source.
In 2024, the landscape of the automotive industry is set to undergo a significant shift with the expected increase in sales of new Electric Vehicles (EVs). This uptrend not only represents a growing demand for electrified alternatives but also forecasts a notable prevalence of these eco-friendly vehicles on the roads and potentially, in repair facilities. Data from Kelley Blue Book reveals that the U.S. witnessed nearly 1.2 million EVs sold in 2023, accounting for 8.1% of the total new vehicle sales—a figure that is projected to rise to a 10% market share in 2024.
With approximately 2.5 million EVs already registered in the United States, they constitute about 1% of the total vehicle population. Interestingly, Canada exhibits a more pronounced enthusiasm towards EVs, with one in 10 Canadians owning an electric vehicle. Despite a perceived dip in interest among Canadian consumers, EVs are expected to comprise more than 10% of Canada’s gross new vehicle sales in the coming year, indicating a faster adoption rate compared to their southern neighbors, according to the U.S. Department of Energy. This burgeoning shift underscores a crucial transition towards sustainability in the North American automotive market.
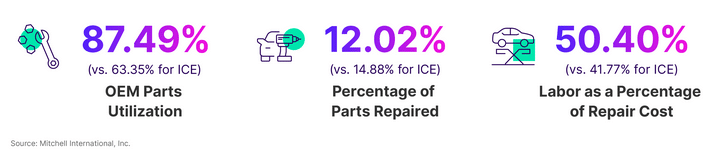
Electric Vehicles (EVs) not only represent a leap toward a greener future but also epitomize the increasing complexity of modern vehicles. Their reliance on advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and the utilisation of lightweight materials significantly complicates their repair processes. For instance, repair estimates for EVs are roughly 50% more likely to involve operations related to sensors than those for 2020 model year and newer Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) vehicles, according to data from 2023. This higher incidence of sensor-related repairs often necessitates ADAS calibrations to ensure the vehicles are safe for road use again, thereby increasing repair times and costs. Additionally, major component sheet metal replacement parts in EVs are identified as lightweight materials—including aluminum, carbon fiber, and composites—26.87% of the time, in contrast to 23.42% for ICE vehicles.
Manufacturers opt for a mixed materials construction strategy in EVs to counterbalance battery weight, amplify range, and enhance performance. However, the repairability and associated costs are impacted due to the specialized nature of these lightweight parts. Furthermore, EVs’ heavier average weight than their ICE counterparts contributes to a higher frequency of airbag deployments (3.62% for EVs compared to 2.45% for ICE vehicles last year), making collision repairs involving airbag deployments considerably more costly. This disparity in repair cost further distinguishes EVs from ICE vehicles, underscoring the evolving challenges within automotive maintenance and repair sectors.
By the Numbers