Less EVs Qualify For Tax Credit, China Proposes Fresh Export Curbs on EV Technology
In 2025, the list of eligible vehicles eligible for the federal tax credit for electric vehicles has become more limited and complicated compared to previous years, with many models no longer currently eligible.
In 2024, significant changes to the U.S. federal tax credit for electric vehicles (EVs) and plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) have made it more challenging to qualify for the $7,500 rebate. While nearly every new EV and PHEV previously qualified for the credit if it was manufactured in North America, the new rules introduced stricter requirements aimed at reducing dependence on China for battery components. To qualify for the full tax credit, a certain percentage of the minerals used in the vehicle’s battery must come from the U.S. or its trade partners. Additionally, the vehicle must be assembled in North America.
The rules also impose income limits for buyers and caps on the price of the vehicles that qualify. This is meant to ensure that the tax credit benefits go primarily to more affordable vehicles rather than luxury models. While some models no longer qualify, there’s potential for more vehicles to be added as automakers adjust their supply chains and manufacturing processes to meet the new criteria.
If you were hoping to rely on the tax credit to help you purchase an EV or PHEV in 2025, it’s essential to stay informed. So, it’s important to keep an eye on the news and regularly check which cars qualify for the tax credit. Additionally, the federal EV tax credit may be cut soon by the incoming administration.

Which EVs Qualify Now?
At the start of 2025, several popular electric vehicle (EV) models have lost eligibility for the federal tax credit, including well-known names like the Tesla Model Y, Chevrolet Bolt, Nissan Leaf, Volkswagen ID.4, Rivian R1T, and Rivian R1S. These vehicles are no longer eligible due to the new rules requiring stricter battery sourcing and manufacturing requirements, aimed at reducing reliance on China for key materials.
The Cadillac Optiq, Hyundai Ioniq 5, Kia EV6, and others qualify, meeting the updated criteria for battery sourcing, assembly location, and vehicle pricing.
This year, several plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) that were once eligible for the federal tax credit are no longer qualifying due to the new rules. Among the most notable exclusions are the Jeep Wrangler 4xe and the Jeep Grand Cherokee 4xe. These models no longer meet the updated criteria, primarily related to battery sourcing and manufacturing requirements. As of now, the only PHEV still eligible for the tax credit is the Chrysler Pacifica minivan. Check fueleconomy.gov to see which EVs currently qualify.
China Proposes Fresh Export Curbs on EV Technology
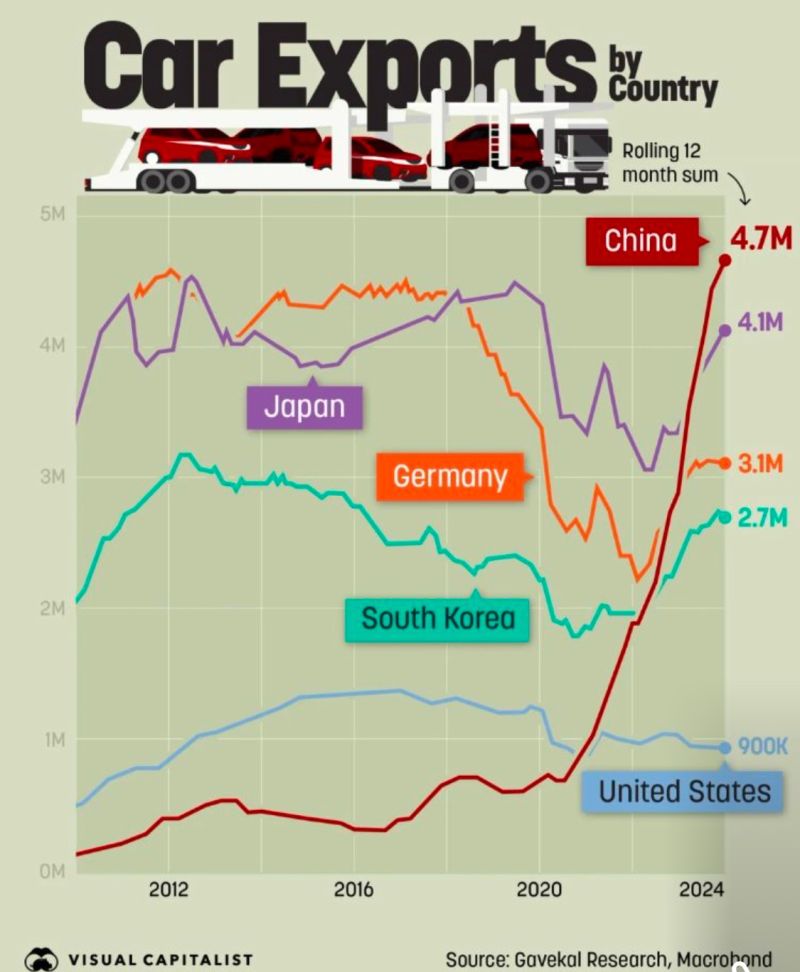
The reasons why less vehicles qualify in 2025 for the federal EV tax credit is because of rising trade tensions between the US and China, the leader of global EV production and technology. The incoming US administration has threatened new tariffs against China, which many experts believe prompted China to propose fresh export curbs on its EV technology this week.
China is planning to curb the export of technology used to extract minerals critical for the growth of the global electric vehicle (EV) industry, as CNN reported on January 3, 2025.
China is considering expanding its export controls to include battery cathode technology, according to a notice published by the country’s Commerce Ministry earlier this week. This proposal is in addition to previously announced restrictions on technologies related to the production of critical materials like lithium and gallium, which are essential for manufacturing semiconductors and electric vehicle (EV) batteries.
Mao Ning, a spokesperson for the Chinese Foreign Ministry, said: “What we can tell you as a principle is that China implements fair, reasonable and non-discriminatory export control measures.”
If the new controls are approved, they would form part of a broader strategy by China to limit the global availability of key technologies and materials used in the production of these advanced products. Battery cathodes, in particular, are crucial components for EV batteries, and restricting their export could have significant implications for global EV production, as well as the broader semiconductor industry. These measures reflect ongoing geopolitical tensions and the increasing importance of securing critical supply chains for emerging technologies, such as EVs.
The latest proposal could be a “resource weaponization” strategy to secure a bargaining chip ahead of the President-elect’s second term, Liz Lee, an associate director at Counterpoint Research, told CNN.
If implemented, a ban or restriction “could significantly strengthen (China’s) dominance in the battery ecosystem, especially to boost its supply chain for EV batteries,” said Lee.
Why America’s Auto Industry Won’t Survive Without Government Help, Such as the Federal EV Tax Credit
The incoming administration has threatened to cut the federal EV tax credit. EVinfo.net strongly believes this is a big mistake.
The federal EV tax credit and EV subsidies are important because they are crucial to helping American automakers catch up to China and compete with China, by producing EVs, hybrids and gas cars made in America.
The reason keeping an eye on EV sales and production in China is important is because it is definitive proof that EVs are rapidly becoming the dominant force in the global automotive industry. America’s automotive OEMs are less able every passing year to compete globally with China’s low vehicle prices, due to the country’s low production costs. America must subsidize its automotive industry to survive and compete. Join our fight to save the credit and subsidies.

Electric Vehicle Marketing Consultant, Writer and Editor. Publisher EVinfo.net.
Services